This project report was compiled as part of the course requirements of CS 6476 Computer Vision under Prof. James Hays
In this project we use convolutional neural networks to classify scenes into categories. In Part 1, we train a neural network from scratch and in Part 2, we use the pretrained VGG network and fine tune it to our data.
Part 1
To start off, we build a CNN ground up and train it.
Data Jittering
As we do not have enough data, we perform data jittering to augment our data set. We perform data jittering by:
- Image flipping: Flip the image horizontally
- Random Image rotation: Rotate the image slightly
- Random Image scaling: Scale the image slightly
Zero centering
To normalize the data set, we subtract the average of the data set from each of the image.
Network Regularization
Regularization is used to fight overfitting of the model to the dataset. We do this by using a dropout layer, which randomly switches connections on and off between layers. This prevents a unit in one layer from relying too strongly on a single unit in the previous layer.
Network Architecture
We train a network to categorize images in the 15 scene categories. The following is the architecture of the network
| layer | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Input | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Dropout | FullConv | Soft Max |
| Details | Input Image | Filter Size: 9 Stride 1 Filters: 10 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Filter Size: 38 Stride 6 Filters: 15 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Rate: 0.5 | Filter Size: 3 Filters: 15 |
|||||
| Dimensions | 64x64x3 | 56x56x10 | 56x56x10 | 11x11x10 | 11x11x10 | 7x7x15 | 7x7x15 | 3x3x15 | 3x3x15 | 3x3x15 | 1x1x15 | 1x1x15 |
Result
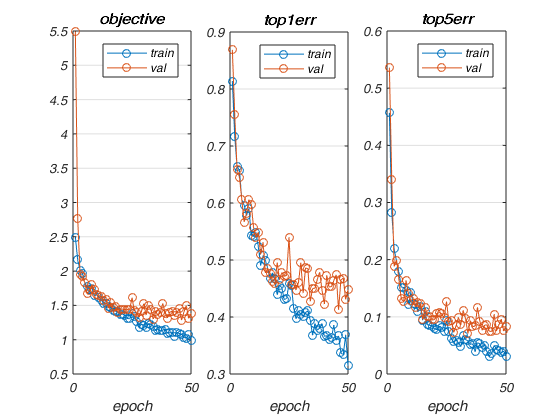
The given network, produces an accuracy of 57.8% with a learning rate of 0.01 in 50 epochs
Architecture Experimentation
The following networks are modified versions of the network specified in the project description. A constant learning rate of 0.001 was used for each of the following networks. The difference in the networks can be realised by examining the 10th layer (Full Conv1)
Full Conv Layer Resolution: 8
| layer | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Input | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Dropout | FullConv | Soft Max |
| Details | Input Image | Filter Size: 9 Stride 1 Filters: 10 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Filter Size: 38 Stride 6 Filters: 8 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Rate: 0.5 | Filter Size: 3 Filters: 15 |
|||||
| Dimensions | 64x64x3 | 56x56x10 | 56x56x10 | 11x11x10 | 11x11x10 | 7x7x8 | 7x7x8 | 3x3x8 | 3x3x8 | 3x3x8 | 1x1x15 | 1x1x15 |
Results
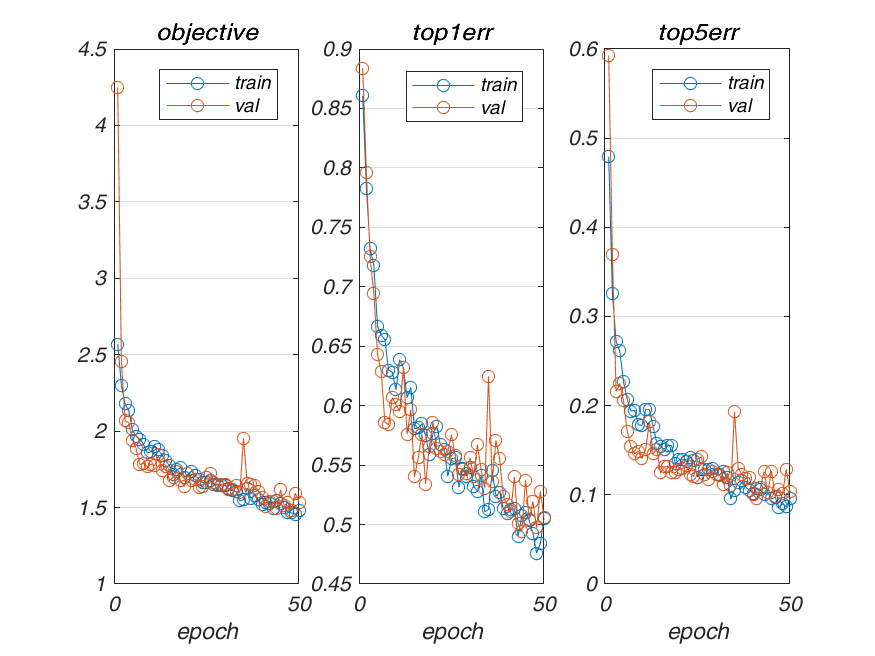
Lowest validation error for above network: 0.494000
Full Conv Layer Resolution: 10
| layer | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Input | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Dropout | FullConv | Soft Max |
| Details | Input Image | Filter Size: 9 Stride 1 Filters: 10 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Filter Size: 38 Stride 6 Filters: 10 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Rate: 0.5 | Filter Size: 3 Filters: 15 |
|||||
| Dimensions | 64x64x3 | 56x56x10 | 56x56x10 | 11x11x10 | 11x11x10 | 7x7x10 | 7x7x10 | 3x3x10 | 3x3x10 | 3x3x10 | 1x1x15 | 1x1x15 |
Results

Lowest validation error for above network: 0.457333
Full Conv Layer Resolution: 12
| layer | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Input | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Dropout | FullConv | Soft Max |
| Details | Input Image | Filter Size: 9 Stride 1 Filters: 10 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Filter Size: 38 Stride 6 Filters: 12 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Rate: 0.5 | Filter Size: 3 Filters: 15 |
|||||
| Dimensions | 64x64x3 | 56x56x10 | 56x56x10 | 11x11x10 | 11x11x10 | 7x7x12 | 7x7x12 | 3x3x12 | 3x3x12 | 3x3x12 | 1x1x15 | 1x1x15 |
Results

Lowest validation error for above network: 0.436000
Full Conv Layer Resolution: 18
| layer | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Input | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Dropout | FullConv | Soft Max |
| Details | Input Image | Filter Size: 9 Stride 1 Filters: 10 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Filter Size: 38 Stride 6 Filters: 18 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Rate: 0.5 | Filter Size: 3 Filters: 15 |
|||||
| Dimensions | 64x64x3 | 56x56x10 | 56x56x10 | 11x11x10 | 11x11x10 | 7x7x18 | 7x7x18 | 3x3x18 | 3x3x18 | 3x3x18 | 1x1x15 | 1x1x15 |
Results

Lowest validation error for above network: 0.412667
Full Conv Layer Resolution: 19
| layer | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Input | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Dropout | FullConv | Soft Max |
| Details | Input Image | Filter Size: 9 Stride 1 Filters: 10 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Filter Size: 38 Stride 6 Filters: 19 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Rate: 0.5 | Filter Size: 3 Filters: 15 |
|||||
| Dimensions | 64x64x3 | 56x56x10 | 56x56x10 | 11x11x10 | 11x11x10 | 7x7x19 | 7x7x19 | 3x3x19 | 3x3x19 | 3x3x19 | 1x1x15 | 1x1x15 |
Results

Lowest validation error for above network: 0.416667
Full Conv Layer Resolution: 20
| layer | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Input | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Conv | BNorm | MaxPool | ReLU | Dropout | FullConv | Soft Max |
| Details | Input Image | Filter Size: 9 Stride 1 Filters: 10 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Filter Size: 38 Stride 6 Filters: 20 |
Pool Size: 6 Pad: 5 Stride: 6 |
Rate: 0.5 | Filter Size: 3 Filters: 15 |
|||||
| Dimensions | 64x64x3 | 56x56x10 | 56x56x10 | 11x11x10 | 11x11x10 | 7x7x20 | 7x7x20 | 3x3x20 | 3x3x20 | 3x3x20 | 1x1x15 | 1x1x15 |
Results

Lowest validation error for above network: 0.436000
Collated Results
The following results are with a learning rate of 0.001 in 50 epochs
| Spatial Resolution | Accuracy(Lowest top 1 err) | Accuracy(Last top 5 err) | Execution Time(secs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.494 | 0.103 | 245.84 |
| 10 | 0.457 | 0.094 | 241.91 |
| 12 | 0.436 | 0.105 | 239.26 |
| 18 | 0.413 | 0.083 | 238.09 |
| 19 | 0.417 | 0.097 | 240.48 |
| 20 | 0.436 | 0.085 | 240.52 |
Learning Rate Experiments
Once the best spatial resolution for the full conv layer was found, the learning rate was chosen by experimenting with multiple values
| Learning Rate | Accuracy (Lowest Validation error) | Learning Rate Curves |
|---|---|---|
| 10-5 | 0.758667 | 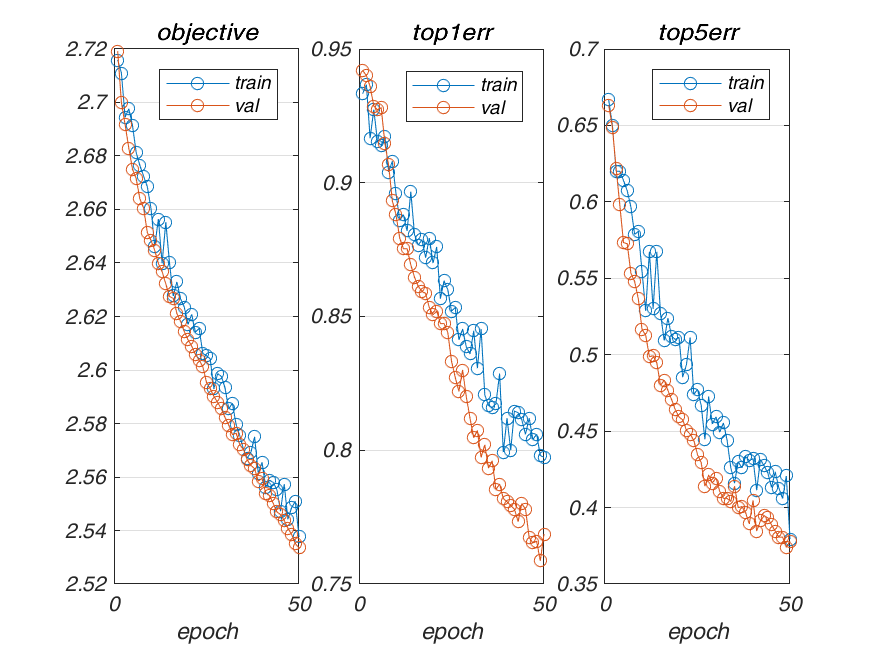 |
| 10-4 | 0.509333 | 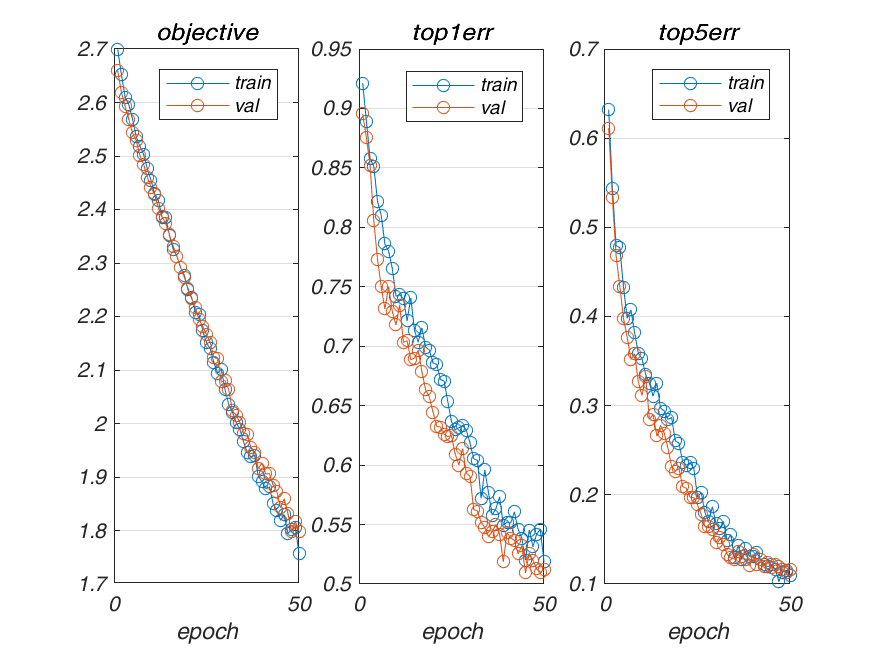 |
| 10-3 | 0.412667 |  |
| 10-2 | 0.412667 | 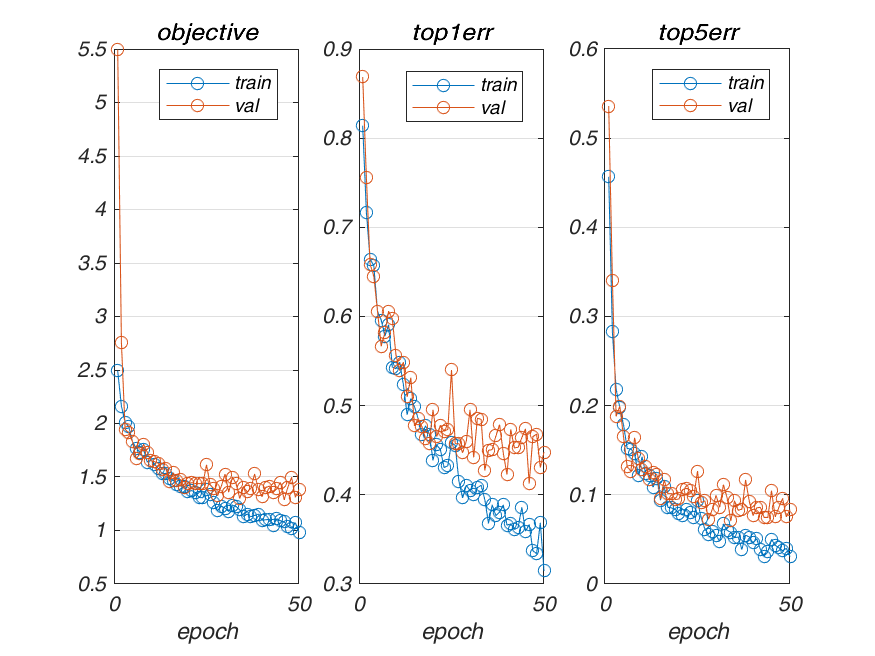 |
| 10-1 | 0.412667 | 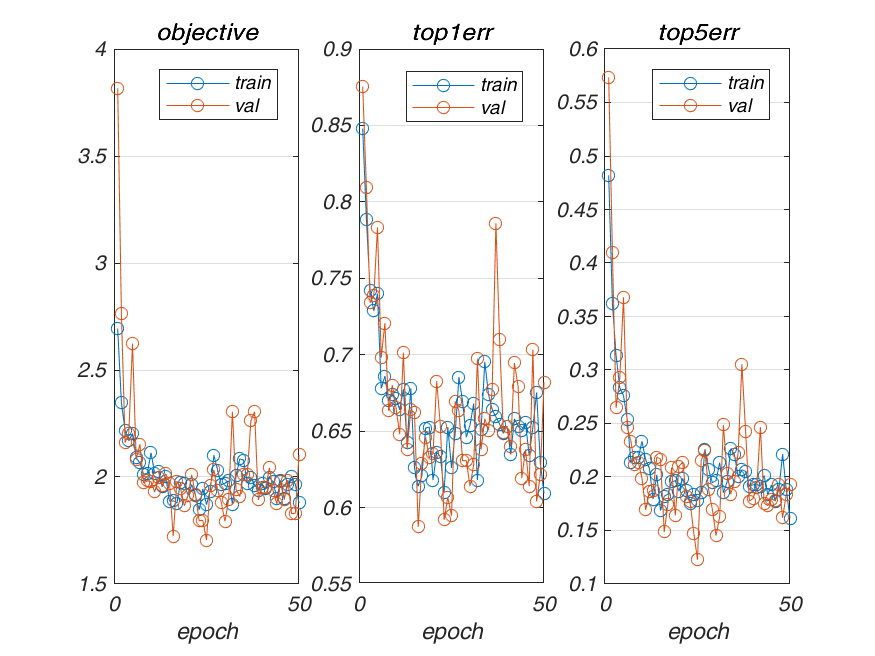 |
Part 2: Transfer Learning
A noteable feature about deep learning is that networks trained for one task can be repurposed for other (similar)tasks and with minor changes and fine tuning, give good results on the “transferred” tasks.
This can be especially useful when the data set required for a certain task is not enough.
We fine tune and modify the trained VGG network to classify our 15 category dataset
The original VGG-16 Network: 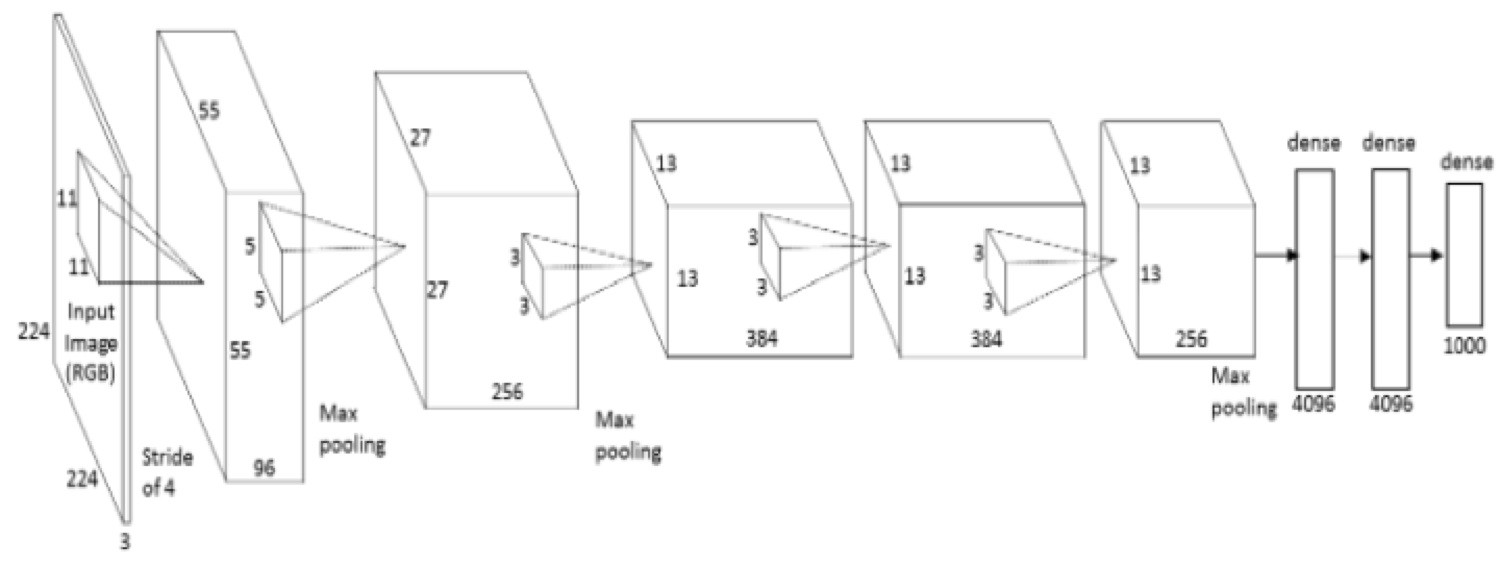
Architecture 1
The following is the first architecture that I tried for part 2. The architecture is based off the VGG network. To build it, the following changes were made to the base network.
- VGG expects 224 x 224 resolution-ed images
- VGG expects 3 channel images(RGB) so update the input code to repeat the grayscale image in all channels.
- Normalize images
- Replace the existing fully conv layer in the last stage of VGG to return a 1 x 15 vector instead of the 1 x 1000 vector
- Replace the softmax layer (this is done to replace the node values in the pretrained layer)
- Add dropout layers between fc6 - fc7 and fc7 - fc8(i.e. new-fc8)
The results of this architecture follow.
Replace the Fully Convolutional Layer by a new(randomly initialized) FC Layer with output size of 4096 x 15
Result
The above network was retrained on the last 9 layers, and an accuracy of the 87.6% was achieved in 5 epochs with a constant learning rate of 0.001
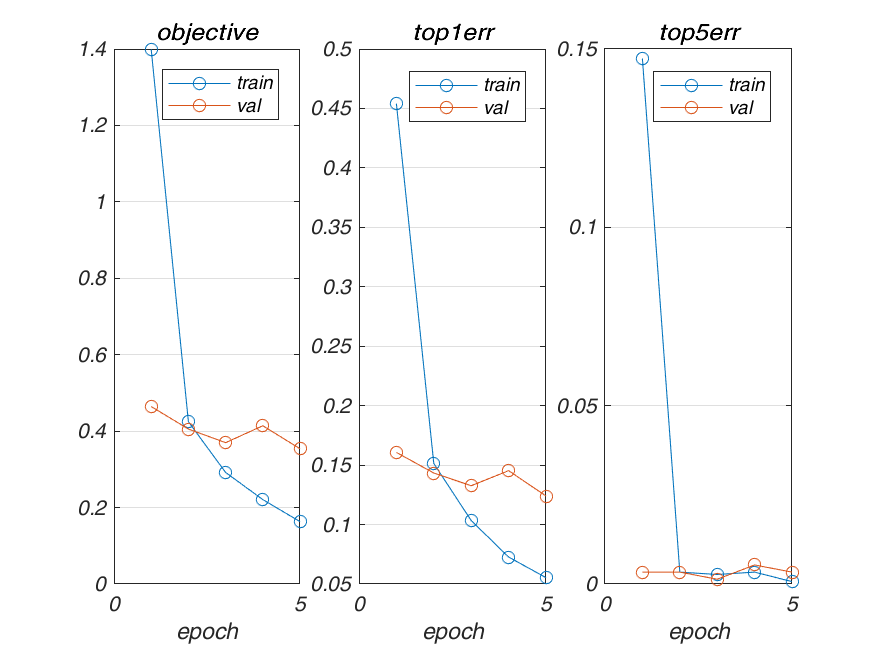
Architecture 1 (with image size jittering)
The above architecture was used with image size jittering to produce the following results:
Result
I added some image size jittering in this part, hoping to gain an increase in accuracy, but it didnt affect the results much.


Accuracy: 86.87% in 5 epochs and 87.3% in 10 epochs
Architecture 2
Tried to add normalization after each conv layer, but failed miserably
Result

Validation Accuracy: 50.6%
Architecture 3 with Backprop Depth: 5
Replace the last Fully Convolutional Layer(FC-8) by a new(randomly initialized) FC Layer with output size of 1024 x 15 and replace the (FC-7) by a new(randomly initialized) FC Layer with output size of 4096 x 1024
Result
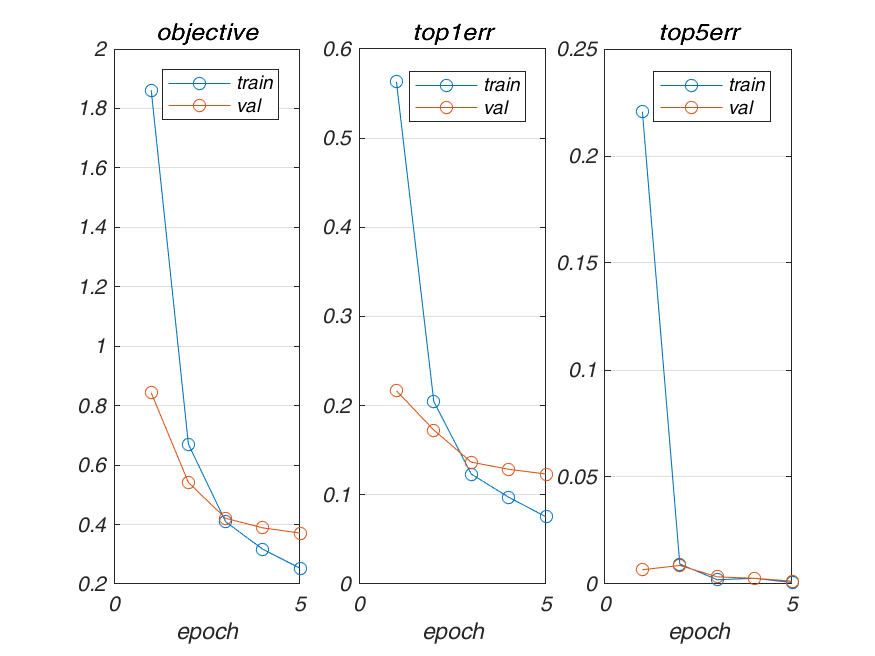
Validation Accuracy in 5 epochs: 87.7% (756.40 secs)
Architecture 3 with Backprop Depth: 6
Result
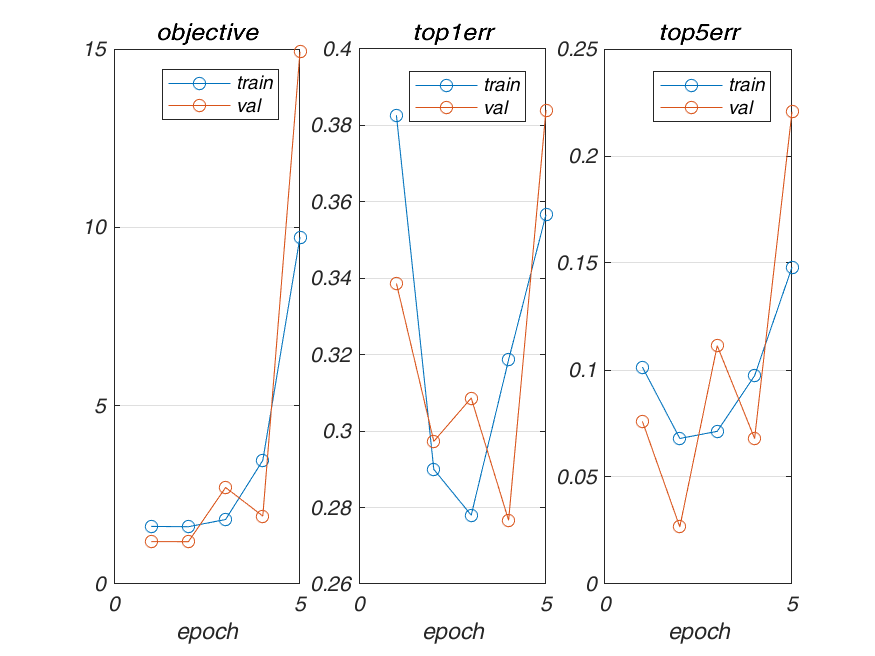
Validation Accuracy: 86.2% in 4 epochs (537.444951 seconds)
Architecture 4
Replaced all fully convolutional layers with 1 fully convolutional layer
Result

Validation Accuracy: 82.66% in 5 epochs (588.709 seconds)
Collated Results
The following results are with a learning rate of 0.001 in 5 epochs
| Network | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Architecture 1 | 87.6% |
| Architecture 1(image size jittering) | 86.8% |
| Architecture 2 | 50.6% |
| Architecture 3(Backprop Depth 5) | 87.7% |
| Architecture 3(Backprop Depth 6) | 86.2% |
| Architecture 4 | 82.6% |
Extra credit
Image sketch token Recognition
We use the data set provided as part of the article: How Do Humans Sketch Objects?
Setup
- Download the image dataset from here The dataset contains 250 image categories and 80 images in each category.
- The images are named as numbers.
- To split into data and train set, I duplicated the folders and called them train and test.
- In train, I delete all images with odd numbered endings and even numbered endings in test
The following shell script can be used to split the dataset into the training and test set
cp -r dataset train
mv dataset test
find train/ -name "*1.png" -delete
find train/ -name "*3.png" -delete
find train/ -name "*5.png" -delete
find train/ -name "*7.png" -delete
find train/ -name "*9.png" -delete
find test/ -name "*0.png" -delete
find test/ -name "*2.png" -delete
find test/ -name "*4.png" -delete
find test/ -name "*6.png" -delete
find test/ -name "*8.png" -delete
I added proj6_extra_credit_setup_data.m, proj6_extra_credit.m, proj6_extra_credit_cnn_init.m for the extra credit section.
I used the VGG network from part2 for this task with minor modifications
- Data Set: As opposed to the given dataset which had 15 categories with 200 images each, the sketch tokens data set has 250 categories with 80 images each. VGG requires that each image be 224 x 224 pixels. Due to memory constraints I choose 50 categories at random and train/test my network on these categories.
- Network Changes: I have used the exact same network from part2, but changed the final layer to predict 250 categories instead of 15.
Results
Validation Accuracy: 74.75%
Hyper Parameters
- Back prop depth: 5
- Learning Rate: 0.001
- Epochs: 10
- Batch Size: 50
References
- S. Liu and W. Deng, “Very deep convolutional neural network based image classification using small training sample size,” 2015 3rd IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition (ACPR), Kuala Lumpur, 2015, pp. 730-734.
- Mathias Eitz, James Hays, and Marc Alexa. 2012. How do humans sketch objects?. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 4, Article 44 (July 2012)