I have been working on this project for a while now. I got my first positive results yesterday.
A raytracer is a light simulation program used in Computer Graphics to achieve a better and more realistic looking output as compared to the other techniques. A raytracer shoots a ray from a said view-point and through every pixel of a viewing plane. These rays return the color of the object they intersect with (black if no object is hit). After intersection with the object they trace the lights to find out if they are in the shadow region of another object. (Shadow region is the region where the light cannot reach the object due to another object in the direction of the light). On the basis of the material’s properties the ray further traces to check for reflections and refractions.
The raytracing algorithm has been criticized for being processor intensive and is hence combined with GPU computing.
The project source code can be found here. The application has been developed in C++. Unlike most raytracers, instead of rendering an image of the output, I have rendered it on the screen using OpenGL(2.x). The program also implements an .obj file importer and is capable of displaying the geometry in both, the raytracer output as well as through the OpenGL routines. The importer uses the winged-edge data structure for the geometry.
The following is the BSOD as mentioned in the first screen.

The following output is the intersection map of the rays with the objects.

This is the output is the combine with the intersection map of the rays with the objects and the shading using the LAMBERT properties for the object materials.
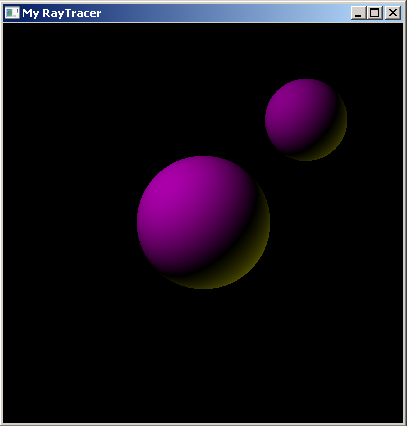
The following resources came in pretty handy during the implementation.
- UC Berkeley CS 184 Raytrace Journal
- UC Berkeley CS 184 Raytracing Resources
- CG Society: Ray Sphere Intersection
- Codermind
Future Work
- Implementing the Ray-Quad intersections for planar objects
- Reflections
- Refractions